This comprehensive furnace buying guide will teach you everything you need to know about selecting the right furnace for your home. Whether you're replacing an existing furnace or installing a furnace for the first time, understanding the different types of furnaces, their efficiency ratings, and other available features will help you make an informed decision.
Quick Recommendations
Before reading our detailed home furnace buying guide, consider these quick recommendations to get started.
Average Users
- Consider a high-efficiency gas furnace for its balance of cost and performance.
- Choose a system with an AFUE rating of at least 90.
- Ensure your home’s ventilation system can support the unit’s requirements.
Large Homes
- Consider a two-stage or modulating furnace for consistent heating and better efficiency.
- Look for units with zoned heating to save money while precisely controlling your home’s climate.
- Ensure the system is powerful enough to heat your home.
Small Rooms/Apartments
- A single-stage furnace might be sufficient.
- Make sure the furnace is not too powerful for your space.
- Look for models with an energy saver mode.
Table of Contents
- Types of Furnaces
- Single Stage Furnaces, Two Stage Furnaces and Modulating Furnaces: Which is Best?
- Understanding AFUE Ratings
- Optimizing Your Furnace’s Performance
- Additional Considerations
- Best Furnace Brands
- Summary

Types of Furnaces

Gas Furnaces
Gas furnaces are the most common type of furnace. They are known for being efficient and cost effective. Gas furnaces operate by burning natural gas to produce heat, which is then distributed throughout your home via a duct system. Because of their reliability and relatively low operating costs, gas furnaces are a great choice for most homes.
Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces use electric heating elements to warm air before pushing it through your home’s ductwork. Generally, they are the cheapest of the four furnace types to purchase and install. They tend to last the longest and do not produce carbon monoxide, making electric furnaces better for your family’s health and the environment.
On the other hand, the higher cost of electricity compared to the other fuel sources make electric furnaces expensive to operate.
Propane Furnaces
Propane furnaces are similar to gas furnaces but use propane as fuel. They are often used in rural areas where natural gas lines are not accessible. Propane furnaces consume less fuel than gas furnaces, meaning you don’t have to burn as much propane as you would to produce the same amount of warmth from a gas furnace.
However, propane furnaces require a storage tank for the propane fuel. You are responsible for refilling and replacing this tank as necessary, which can lead to propane furnaces costing more than gas furnaces when used regularly.
One notable feature is that propane furnaces do not require a flue and can be vented directly through an exterior wall.
Single Stage Furnaces, Two Stage Furnaces and Modulating Furnaces: Which is Best?
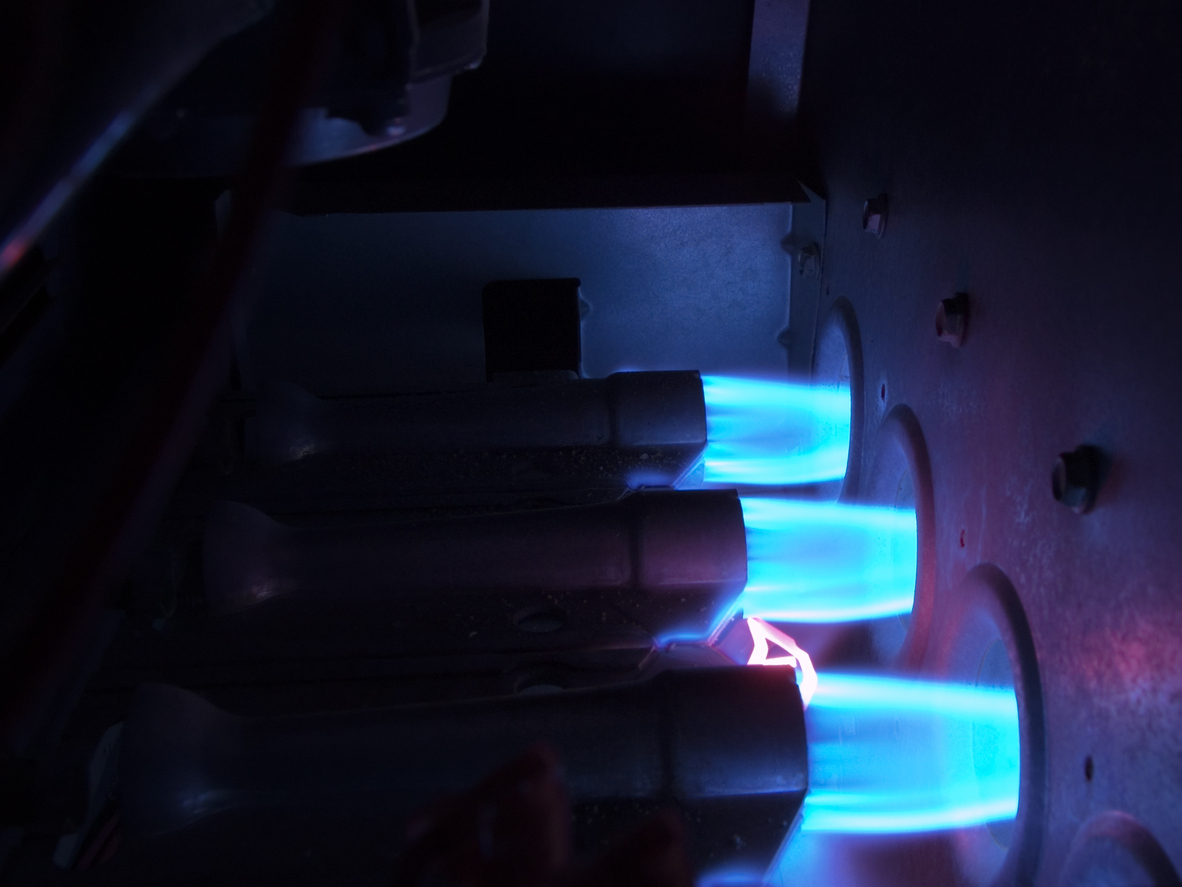
In addition to choosing between fuel sources, you also need to consider how many stages you want your furnace to have. Currently, there are three options on the market.
Single Stage Furnaces
Single-stage furnaces have only one flame setting. This means they can only be on or off. Single stage furnaces are less precise when maintaining temperature and tend to cycle on and off more frequently, which can lead to inefficiency and uneven heating.
However, single stage furnaces are cheaper and simpler to install, making them an economical choice for many.
Two Stage Furnaces
Two stage furnaces have two flame settings, allowing them to operate at a lower setting when the weather is mild and a higher setting when the weather is cold. This makes them more efficient and better at maintaining a consistent temperature than single-stage furnaces.
While two stage furnaces are more expensive to purchase and install, the energy savings associated with them can help you recoup the cost. This is especially true for those who live in colder climates.
Modulating Furnaces
Modulating furnaces offer the most precise temperature control of the three furnace subtypes. They work by continuously adjusting the flame size to match the desired thermostat setting.
Modulating furnaces are the most expensive but provide the best comfort and performance. An HVAC technician will help you determine whether a modulating furnace is right for your home.
Understanding AFUE Ratings

Gas furnaces are the most popular type of furnace, and the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating measures the efficiency of gas furnaces. Think of your system’s AFUE rating as a percentage representing the amount of fuel converted into usable heat. A higher AFUE rating indicates greater energy efficiency, which translates to lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills.
Technological advancements have made furnaces more efficient over the years. Gas furnaces from the 1970s typically have AFUE ratings of 65. For new gas furnaces, the lowest AFUE permitted by law is 80. Some top of the line models cap out at 98.5 AFUE.
Generally, the more fuel efficient a furnace is, the more expensive it will be. A furnace with a 90 AFUE rating can cost up to $1,000 more than a similarly sized unit with an 80 AFUE rating.
This higher upfront cost can be easily recouped over time, especially in colder regions. Keep in mind that the quality of your home’s insulation and your local gas and electricity rates will impact this timeline.
Modern gas furnaces typically have AFUE ratings between 80 and 90. When choosing a furnace, opting for a unit with a high AFUE rating will be beneficial in the long term.
Keep in mind that electric furnaces have an AFUE rating of 100.
Optimizing Your Furnace’s Performance

Ductwork
Your furnace needs ductwork to properly distribute heat throughout your home. If you live in a newer home, your ductwork is likely already in good condition. However, if you are having a new furnace installed, you will still want to have a licensed HVAC technician make sure your ductwork is equipped to handle your new furnace.
Ductwork is to blame for many furnace issues. An HVAC technician can determine if your ductwork was installed correctly, or if there are any leaks or blockages impairing its function. In many cases, improving the efficiency of your heating system will only require you to seal leaks in your ductwork (rather than replacing the entire system).
Vents
Furnaces use toxic natural gas to produce heat energy. To prevent this gas from leaking into your home, your furnace is equipped with an exhaust pipe that vents this gas outside.
Since old furnaces and new furnaces vent gas differently, it is important to ensure that your home’s ventilation system is functioning as intended. Talk to your HVAC contractor to make sure all aspects of your ventilation system are correct.
Humidifiers
Furnaces can dry out the air in your home, leading to issues such as sinus infections. Installing a furnace humidifier can mitigate this problem. The cost of a furnace humidifier varies widely, from as little as $200 to as much as $1,600. You can also place single humidifiers in individual rooms.
Additional Considerations
Energy Efficiency
Look for units with the Energy Star certification. This indicates that the unit meets or exceeds energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Energy-efficient furnaces not only reduce your carbon footprint but also lower your energy bills.
Some furnaces come with programmable thermostats, allowing you to set specific temperatures for different times of the day, further increasing your energy savings.
Features
Modern furnaces come with various features that provide comfort and convenience.
Zoned Heating
Zoned heating systems utilize multiple thermostats, dampers that regulate airflow, and an advanced central controller to provide varying levels of heat to different areas of the house. They are especially useful in large residencies, where heating the entire home would be a waste of resources.
Variable Speed Blowers
When less heat is needed, variable speed blowers slow down, delivering air more gradually and producing less noise. This keeps drafts and temperature fluctuations at a minimum.
Variable Heat Output
Some furnaces equipped with variable speed blowers can vary the amount of heat they deliver (usually between two levels). This can lead to superior heating consistency and energy efficiency when compared to furnaces with fixed heat outputs.
Dual Heat Exchanger
The highest efficiency furnaces are equipped with a secondary heat exchanger. As burned natural gas leaves the primary heat exchanger, it enters the secondary heat exchanger. The secondary heat exchanger absorbs the remaining heat from the burned natural gas, cooling and condensing the gas. The extra heat is circulated throughout your home while the condensate and remaining gasses are expelled.
Ignition System
A pilot light is a continuously burning flame that is always available to light the burners. However, modern systems have mostly done away with pilot lights, instead relying on electronic ignition systems. These electric ignition systems are more efficient than pilot lights, and this increased efficiency will be reflected in the furnace’s AFUE rating.
Air Filtration
Reduce the volume of dust in your heating system by fitting your furnace with an electrostatic filter or a HEPA filter. Filtering your air in this manner is especially beneficial for those with allergies, asthma, or chronic lung diseases.
Warranty
Warranty coverage is an important factor when choosing a furnace. Some manufacturers offer long warranties that cover parts and labor, providing peace of mind and protection against potential issues. Check the manufacturer’s website and ask the retailer about the warranty for the model you are considering.
Best Furnace Brands
To ensure long-term performance and efficiency, you will want to choose a reliable furnace brand. The following manufacturers have a reputation for producing quality, highly efficient products:
- Lennox
- Goodman
- York
Summary
Choosing the right furnace for your home involves understanding the different types of furnaces and their capabilities. Gas, oil, electric, and propane furnaces each have their own benefits and drawbacks. You will also want to consider factors like cost, energy efficiency, and additional features when buying a new furnace.
By selecting a reliable brand and choosing the right partner for installation and maintenance, your home will remain warm and comfortable for years to come.
For personalized assistance, contact Wolfgangs Cooling, Heating & Plumbing at (928) 767-8905. Our HVAC experts are ready to help you find the best home furnace to address your individual needs.